

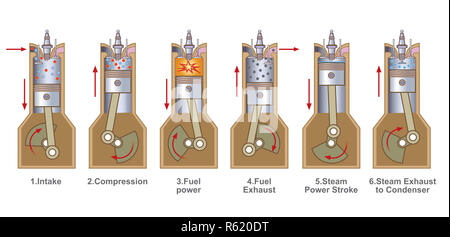
The injected water gradually converts to steam without first exhausting the ignited air fuel mixture, thereby generating an additional power stroke. A central processor is responsive to signals received from a sensor assembly mounted on the internal combustion engine at strategic locations so as to determine the energy content within the one or more cylinders and thereby regulate and control the timing and quantity of the injected water. An injection assembly is connected to each of the piston and cylinder assemblies and structured to inject water into the cylinder during a predetermined portion of the six-stroke cycle. An injection assembly is connected to each of the piston and cylinder assemblies and structured to inject water into the cylinder during a predetermined portion.Īn internal combustion engine and its method of operation which is designed to operate on a six-stroke cycle and which may include at least one but preferably a plurality of piston and cylinder assemblies each of which are characterized by a cylinder having a piston reciprocally mounted therein and intake an exhaust valves cooperatively mounted to regulate fluid flow into and out of the cylinder. Typical combustion mean effective pressures (MEP combustion) of naturally aspirated gasoline engines are up to 10 bar, thus this concept has the potential to significantly increase the engine efficiency and fuel economy.An internal combustion engine and its method of operation which is designed to operate on a six-stroke cycle and which may include at least one but preferably a plurality of piston and cylinder assemblies each of which are characterized by a cylinder having a piston reciprocally mounted therein and intake an exhaust valves cooperatively mounted to regulate fluid flow into and out of the cylinder. The range of MEP steam calculated for the geometry of a conventional gasoline engine and is from 0.75 to 2.5 bars. The valve closing timing for maximum MEP steam is limited by either 1 bar or the dew point temperature of the expansion gas/moisture mixture when the exhaust valve opens. By changing the exhaust valve closing timing during the exhaust stroke, the optimum amount of exhaust can be recompressed, maximizing the net mean effective pressure of the steam expansion stroke (MEP steam). An ideal thermodynamics model of the exhaust gas compression, water injection and expansion was used to investigate this modification. Waste heat from two sources is effectively converted into usable work: engine coolant and exhaust gas. A partial exhaust event coupled with water injection adds an additional power stroke. It can be thought of as a four-stroke Otto or Diesel cycle followed by a two-stroke heat recovery steam cycle. A concept adding two strokes to the Otto or Diesel engine cycle to increase fuel efficiency is presented here.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
